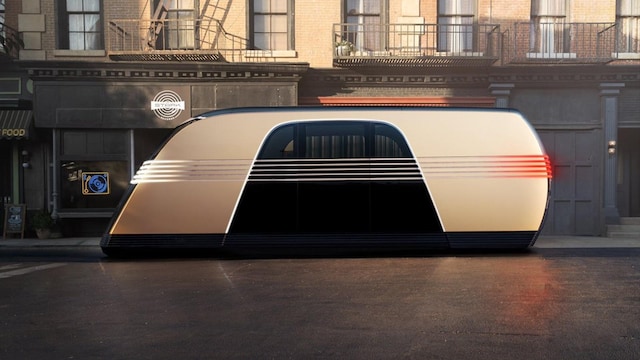
Elon Musk unveiled Tesla’s robotaxi on Thursday (October 11), that includes two gull-wing doorways and no steering wheel or pedals. He additionally launched a robovan, highlighting Tesla’s shift from inexpensive, mass-market automobiles to robotics.
Musk arrived on stage in what he referred to as a “Cybercab,” which is ready for manufacturing in 2026 and priced beneath $30,000. He estimated working prices would ultimately attain 20 cents per mile, with inductive charging eliminating the necessity for plugs.
Click on right here to attach with us on WhatsApp
In keeping with Musk, these automobiles function utilizing synthetic intelligence and cameras with out the additional {hardware} employed by opponents. Nevertheless, traders and analysts have raised considerations in regards to the feasibility of this method from each technical and regulatory standpoints.
Musk’s robotaxi initiatives miles behind China
Regardless of these developments, Tesla lags within the robotaxi house, significantly in China, a vital marketplace for the US automaker. Chinese language startups and tech companies are already testing self-driving fleets in cities like Guangzhou, Wuhan, and Beijing, with assist from native governments.
WeRide, a Guangzhou-based startup, launched in 2017 and has established business operations. Pony.ai, one other autonomous car startup backed by Toyota, holds permits for business robotaxi providers in key Chinese language cities, together with Shanghai and Shenzhen.
)
Tesla’s Robotaxi (X/Tesla)
Main tech firms are becoming a member of the race as properly. Baidu’s Apollo Go service gives totally driverless rides in Wuhan, Beijing, Chongqing, and Shenzhen, with security drivers working in different areas. Baidu reported almost 900,000 rides within the second quarter of 2024, marking a 26 % year-on-year improve.
These Chinese language firms are additionally eyeing worldwide growth. WeRide secured a allow to function within the UAE in early 2023 and not too long ago partnered with Uber to combine its robotaxis into Uber’s platform, with a rollout deliberate later this 12 months. WeRide has additionally acquired permission to check a robobus in Singapore.
Baidu is reportedly in talks with abroad automakers and ride-sharing firms to broaden its providers internationally, with plans to enter markets like Hong Kong, Singapore, and the Center East. Pony.ai, too, is contemplating growth to Southeast Asia, Europe, and the Center East. The corporate has signed a memorandum of understanding with ComfortDelGro in Singapore, doubtlessly paving the way in which for large-scale business operations.
Chinese language startups are additionally testing their applied sciences within the US. WeRide acquired a allow in August to check automobiles in California, permitting passenger transport, with or with out a driver, for the following three years. Nevertheless, these checks are restricted to non-commercial use.
In China, Tesla is reportedly set to obtain preliminary approval to launch its Full Self-Driving service following Musk’s sudden go to to the nation in April. State media has indicated that Tesla is exploring the testing of its autonomous driving software program in Shanghai, with plans to launch by early 2025. Tesla’s China-made electrical car gross sales grew by 19.2 per cent in September in comparison with the identical month the earlier 12 months, in response to the China Passenger Automotive Affiliation.
Profitability downside in robotaxis
Whereas the robotaxi sector is increasing, profitability stays a priority. In keeping with estimates from Haitong Worldwide Securities, Baidu’s Apollo Go service loses almost $11,000 per car yearly in Wuhan, though a inexpensive mannequin may doubtlessly flip a revenue of $16,000 per car annually. Compared, conventional ride-hailing automobiles generate roughly $15,000 yearly, which is cut up between the motive force and platform.
The rise of robotaxis has additionally challenged China’s ride-hailing workforce, which has grown from 4.4 million drivers two years in the past to 7 million right this moment. With the potential for job losses resulting from automation, social media discussions have questioned whether or not driverless vehicles are taking away jobs.
This shift is affecting China’s driving colleges as properly. As an example, Jap Pioneer Driving College has lowered its variety of instructors by greater than half since 2019, changing them with remote-monitoring techniques that permit instructors to guage college students’ driving duties, equivalent to parallel parking, by real-time digital suggestions.
Will the US face comparable challenges sooner or later? Solely time will inform.
First Revealed: Oct 11 2024 | 12:48 PM ist
Thanks for taking the time to learn this text! I hope you discovered the data insightful and useful. If you happen to loved any such content material, please contemplate subscribing to our e-newsletter or becoming a member of our neighborhood. We’d like to have you ever! Be at liberty to share this text along with your family and friends, who may additionally discover it attention-grabbing.

Rishabh Singh is the Editor-in-Chief and CEO of Latestnews24.com. He has also completed his graduation in BSC Aviation and has 2+ years of experience in blogging and digital marketing. Have worked with many businesses and blogs, He is also interested in Entertainments/movies/web stories and new foods recipes news, Actually this is his favorite subject. So he is always ready for discussion and written about this topic.